Have you ever wondered what happens to tritium over time? Tritium decay is a fascinating process that affects everything from nuclear science to everyday technology.
Understanding how tritium breaks down can give you insights into its uses and safety. You’ll discover the simple science behind tritium decay and why it matters to you. Keep reading, and you might be surprised by how this tiny atom impacts the world around you.

Tritium Basics
Tritium is a rare form of hydrogen. It has unique features that make it interesting to scientists. This section explains the basic facts about tritium. It covers its properties and where it comes from.
Understanding these basics helps to learn about tritium decay. It also shows why tritium is important in science and industry.
Properties Of Tritium
Tritium is a radioactive isotope of hydrogen. It has one proton and two neutrons in its nucleus. This makes it heavier than normal hydrogen.
Tritium emits low-energy beta particles. It has a half-life of about 12.3 years. This means it slowly changes into helium-3 over time.
Tritium is colorless, odorless, and non-toxic in small amounts. It combines easily with oxygen to form tritiated water. This water behaves like normal water but contains radioactive tritium.
Sources Of Tritium
Tritium forms naturally in the upper atmosphere. Cosmic rays hit nitrogen atoms and create tritium. It then falls to Earth with rain.
Human activities also produce tritium. Nuclear reactors and weapons tests release it. It appears in small amounts near these sites.
Tritium can be made in laboratories. Scientists use it in research and some industrial applications. Its controlled production helps limit environmental impact.
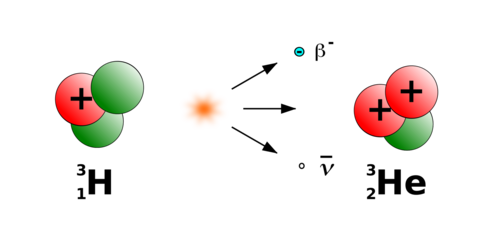
Decay Process
Tritium decay is a natural process that changes this radioactive form of hydrogen. It slowly transforms into a different element by releasing particles. Understanding how this happens helps us learn about radiation and its effects.
The decay process involves tiny particles and energy changes inside the atom. These changes make tritium unstable, leading it to lose some parts and become more stable.
Beta Decay Mechanism
Tritium undergoes beta decay, a type of radioactive decay. It emits a beta particle, which is an electron, from its nucleus. This happens because a neutron in the nucleus changes into a proton. The proton stays inside, and the electron is released.
This emission causes tritium to turn into helium-3, a stable isotope. The process releases energy but no harmful gamma rays. Beta decay explains how tritium changes over time.
Half-life Of Tritium
The half-life is the time it takes for half of the tritium to decay. For tritium, this period is about 12.3 years. This means after 12.3 years, half of the original tritium atoms have changed into helium-3.
Knowing the half-life helps in many fields, like environmental science and nuclear studies. It shows how long tritium remains active and when it becomes safe.
Environmental Impact
Tritium is a radioactive form of hydrogen. It naturally occurs in small amounts but can increase due to human activities. Understanding its environmental impact is important for safety and health.
Tritium can spread through water and air. It slowly decays, releasing low-energy radiation. This radiation can affect living things and the environment around us.
Tritium In Water And Air
Tritium often enters the environment through water. It mixes easily with water molecules. This makes it hard to remove once it is in rivers or lakes.
In the air, tritium appears as tritiated water vapor. It can travel long distances with the wind. Rain can bring tritium back to the ground, spreading contamination further.
Water sources near nuclear plants may have higher tritium levels. Monitoring these levels helps protect wildlife and people. Drinking water safety is a key concern in affected areas.
Radiation Safety Concerns
Tritium emits beta particles, which are weak radiation. This radiation cannot penetrate skin deeply. Still, it can be harmful if ingested or inhaled.
People can absorb tritium by drinking contaminated water or breathing air with tritiated vapor. Long-term exposure may increase health risks. Safety rules limit tritium release to protect communities.
Workers in nuclear industries use special gear to avoid tritium exposure. Public health agencies track tritium to prevent unsafe levels. Keeping tritium under control safeguards both nature and humans.
Applications Of Tritium
Tritium is a rare, radioactive form of hydrogen. It has many important uses across different fields. Its unique properties make it valuable in science and technology. Below are some key applications of tritium.
Use In Nuclear Fusion
Tritium is essential in nuclear fusion research. It acts as a fuel in fusion reactors. When combined with deuterium, it produces high energy. This energy could become a clean power source. Scientists study tritium to improve fusion reactor designs. Its role is critical for future energy solutions.
Tritium In Self-luminous Devices
Tritium glows without electricity. It emits light through radioactive decay. This property is used in self-luminous signs and watches. These items glow in the dark for many years. Tritium lighting is safe and reliable. It helps people see in dark or emergency situations.
Medical And Scientific Uses
Tritium labels molecules to track chemical reactions. This helps scientists study biological processes. It is used in medical imaging and research. Tritium also helps measure the age of samples. Its use assists in understanding diseases and developing treatments. Scientists rely on tritium for precise and safe experiments.
Handling And Storage
Handling and storage of tritium demand careful attention. Tritium is a radioactive form of hydrogen. It emits low-energy beta particles that can be hazardous. Safe practices reduce risks to health and the environment. Proper containment and following rules are essential.
Containment Methods
Tritium is often stored in sealed containers. These containers prevent leaks and exposure. Materials like stainless steel or glass are common choices. Containers must be airtight to stop gas from escaping. Storage areas should have good ventilation. Monitoring equipment detects any possible leaks quickly. Workers must wear protective gear when handling tritium. This includes gloves and lab coats. Preventing skin contact and inhalation is crucial.
Regulatory Guidelines
Many countries have strict rules for tritium use. These rules limit how much can be stored. They also set standards for container quality. Regular inspections ensure compliance with safety laws. Training workers in safe handling is mandatory. Records of tritium amounts must be kept accurate. Emergency plans are required in case of spills. Following these rules protects people and the planet.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Tritium Decay And How Does It Occur?
Tritium decay is the process where tritium emits a beta particle to become helium-3. It occurs naturally and involves a neutron transforming into a proton, releasing energy.
How Long Is The Half-life Of Tritium Decay?
The half-life of tritium decay is approximately 12. 3 years. This means half of a tritium sample decays into helium-3 in that time frame.
What Are The Uses Of Tritium Decay In Industry?
Tritium decay is used in self-luminous devices, like watch dials and exit signs. Its beta radiation provides a steady light source without electricity.
Is Tritium Decay Harmful To Human Health?
Tritium emits low-energy beta radiation, which is minimally harmful externally. However, ingesting or inhaling tritium can pose health risks due to internal exposure.
Conclusion
Tritium decay shows how unstable atoms change over time. It releases low-energy radiation, which has specific uses in science and industry. Understanding this process helps in fields like nuclear energy and medicine. Tritium’s half-life tells us how long it takes to reduce by half.
This knowledge guides safety and handling practices. Studying tritium decay also helps track environmental changes. Overall, it is a small but important part of nuclear science.
Apply for this vacancy
For more information
For more information, please don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re here to assist with any questions or provide additional details to help you make informed decisions. Reach out today, and let’s connect!
Please mention the respective article number.
For more information
For more information, please don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re here to assist with any questions or provide additional details to help you make informed decisions. Reach out today, and let’s connect!
Please mention the respective article number.

