Have you ever wondered what risks come with Tritium, a substance often used in glow-in-the-dark products? While it sounds harmless, Tritium can pose serious dangers to your health and the environment if not handled properly.
Understanding these risks is crucial for your safety and those around you. Keep reading to uncover the hidden threats of Tritium and learn how to protect yourself from its potential harm.

What Is Tritium
Tritium is a rare form of hydrogen. It has an extra neutron in its nucleus. This makes it radioactive. Tritium occurs naturally but in very small amounts. Humans also produce it for certain uses. Understanding tritium helps us see why it can be dangerous.
Basic Properties
Tritium is a hydrogen isotope with one proton and two neutrons. It is radioactive and emits low-energy beta particles. Its half-life is about 12.3 years. Tritium is colorless and odorless. It usually exists as a gas or combined with oxygen to form tritiated water.
Common Uses
Tritium is used in self-powered lighting. It glows without electricity, ideal for watches and exit signs. It also helps in scientific research as a tracer. Nuclear weapons and fusion reactors use tritium too. These uses make handling tritium important for safety.
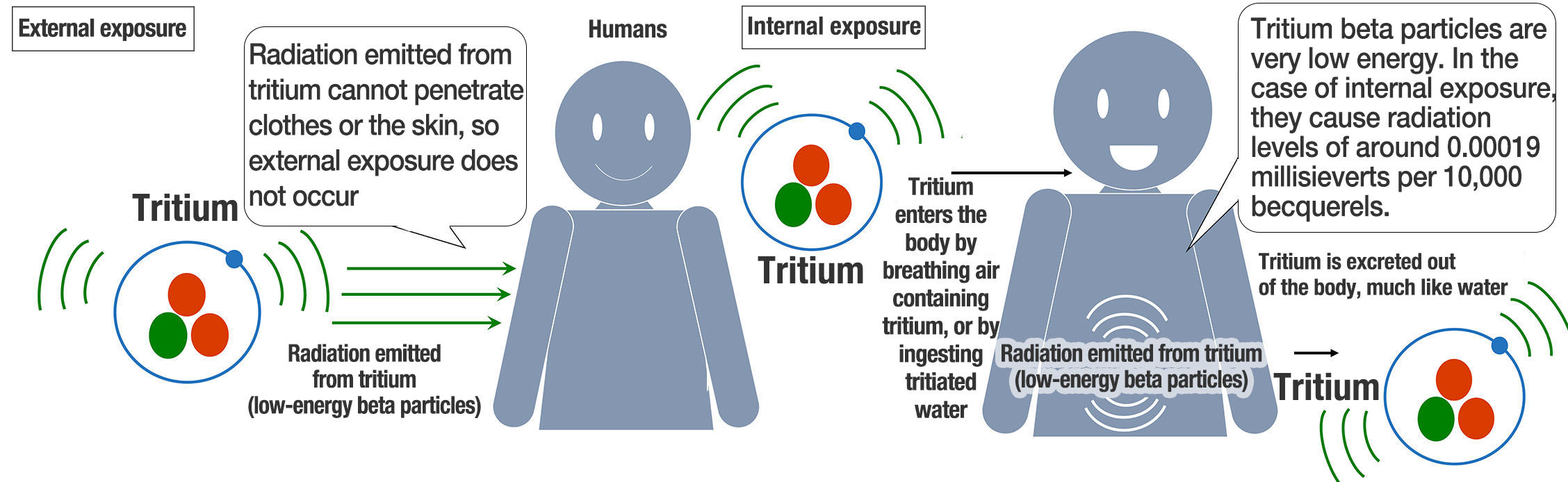
Health Risks Of Tritium
Tritium is a radioactive form of hydrogen. It poses health risks due to its radiation. Understanding these risks helps protect people from harm.
Exposure to tritium can happen through air, water, or food. The level of danger depends on how much tritium enters the body. Even small amounts can affect health over time.
Radiation Exposure Effects
Tritium emits low-energy beta radiation. This radiation cannot penetrate the skin deeply. The main risk occurs if tritium is inhaled or swallowed. Once inside, it can damage cells and tissues. This damage can cause sickness or increase cancer risk.
Short-term exposure may cause mild symptoms. These include nausea, fatigue, or skin irritation. Such effects usually happen with high tritium levels. Most people exposed to low levels feel no symptoms.
Long-term Consequences
Long-term exposure to tritium radiation can be more serious. It may lead to genetic mutations and cell damage. These changes increase the chance of cancer later in life. The risk grows with the amount and length of exposure.
Children and pregnant women are more sensitive to radiation. Their cells divide faster, making damage more harmful. Protecting vulnerable groups from tritium exposure is important. Regular monitoring and safety measures reduce long-term health risks.
Environmental Impact
Tritium, a radioactive form of hydrogen, affects the environment in several ways. Its presence in water, air, and soil raises concerns. Understanding how tritium enters ecosystems and impacts living organisms is vital for safety and health.
Contamination Sources
Tritium mainly comes from nuclear power plants and weapons testing. It also appears in some industrial processes and medical uses. Tritium leaks can occur during production, storage, or disposal. These leaks spread tritium into nearby water bodies and soil. Rain and groundwater can carry tritium far from the original source. Even small amounts can lead to measurable contamination in the environment.
Effects On Ecosystems
Tritium mixes easily with water, entering plants and animals. It can replace normal hydrogen in molecules, altering biological functions. Exposure to tritium may harm aquatic life and reduce biodiversity. Small creatures and plants often absorb the highest levels. This contamination can move up the food chain, affecting larger animals. Long-term tritium presence weakens ecosystems and reduces their resilience.

Safety Standards And Regulations
Tritium is a radioactive material that requires strict safety controls. Governments and agencies set rules to protect people and the environment. These rules limit exposure and guide safe handling of tritium. Understanding these safety standards helps reduce risks linked to tritium.
Safety standards cover allowed tritium levels and how to track them over time. These rules aim to keep exposure as low as possible. They also ensure quick action if tritium leaks or spills occur.
Legal Limits
Legal limits set the maximum tritium allowed in air, water, and soil. These limits protect public health and the environment. Limits vary by country but often follow global guidelines. For example, drinking water usually has strict tritium limits to prevent harm. Factories and labs must follow these limits during operations. Violating limits can lead to fines and shutdowns.
Monitoring Practices
Monitoring tracks tritium levels in places like water sources and workplaces. Regular checks catch leaks early and prevent exposure. Monitoring uses tools like air samplers and water tests. Data from monitoring helps experts assess safety and compliance. Workers in tritium areas wear devices to measure personal exposure. This practice ensures they stay within safe limits.
Handling And Storage Guidelines
Handling and storing tritium safely is very important. Tritium is a radioactive material and needs careful control. Proper guidelines reduce risks to people and the environment. Clear rules help manage tritium in labs, factories, or any place it is used.
Following strict handling and storage steps keeps tritium contained. It prevents leaks and contamination. Safe storage also limits exposure to radiation. Everyone working with tritium must know these rules well.
Protective Measures
Wear protective clothing like gloves and lab coats. Use safety goggles to protect eyes from accidental splashes. Work in well-ventilated areas to avoid inhaling tritium gas. Use sealed containers that prevent tritium release. Always check containers for leaks before use. Store tritium in cool, dry places away from heat. Limit access to trained and authorized people only. Follow all safety signs and instructions strictly.
Disposal Methods
Dispose of tritium waste through licensed facilities only. Do not throw tritium materials in regular trash. Use designated containers for radioactive waste collection. Label all waste containers clearly with tritium warnings. Store waste safely until it is collected. Follow local laws and regulations for radioactive waste disposal. Document all disposal actions for safety records. Proper disposal protects people and the environment from harm.
Emergency Response To Tritium Exposure
Exposure to tritium requires quick and careful action. Tritium is a radioactive form of hydrogen. It can enter the body through the skin, lungs, or mouth. Emergency response helps reduce health risks and prevent contamination. Knowing the right steps saves lives and limits damage.
Immediate Actions
First, move away from the tritium source. Avoid touching your face or other body parts. Remove any contaminated clothing carefully. Wash exposed skin with soap and water right away. Use plenty of water to rinse the eyes if they are affected. Seek fresh air if you inhaled tritium gas. Report the incident to emergency personnel quickly. Follow all safety instructions from professionals at the scene.
Medical Treatments
Doctors will assess your exposure level and symptoms. Blood and urine tests check for tritium inside the body. Treatment focuses on removing tritium and reducing radiation effects. Drinking lots of fluids helps flush tritium from the body. In severe cases, medical staff may use special therapies. Monitoring continues to watch for delayed health problems. Mental support is important to manage stress after exposure.
Future Outlook On Tritium Use
The future of tritium use involves balancing its benefits and risks carefully. Tritium provides unique advantages in lighting and scientific fields. Yet, concerns about its safety and environmental impact remain. Advances in technology aim to reduce these risks. New methods and alternatives are being explored to ensure safer use.
Innovations In Safety
Researchers develop better ways to contain tritium. Improved barriers and detection systems help prevent leaks. Safer handling procedures reduce exposure for workers. Monitoring technology tracks tritium levels in real time. These innovations make tritium use more controlled and secure.
Alternative Technologies
Scientists seek other materials that do not pose risks. Some alternatives offer similar brightness without radioactivity. LED lights and phosphorescent materials gain popularity. These options reduce dependence on tritium. They also help protect the environment and human health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Main Health Risks Of Tritium Exposure?
Tritium exposure can lead to internal radiation damage. It primarily affects cells by emitting low-energy beta particles. Prolonged exposure may increase cancer risk and cause genetic mutations. Avoiding ingestion or inhalation of tritium is essential for safety.
How Does Tritium Enter The Human Body?
Tritium can enter the body through inhalation, ingestion, or skin absorption. Contaminated water, air, or food are common sources. Once inside, it distributes quickly and emits radiation, damaging tissues. Proper containment and protective measures reduce exposure risk significantly.
Is Tritium Dangerous In Small Amounts?
Small amounts of tritium are generally low risk due to weak radiation. However, prolonged or repeated exposure can accumulate, causing health issues. Safety guidelines recommend minimizing contact to prevent potential long-term effects. Always follow regulatory limits to ensure safety.
Can Tritium Exposure Cause Cancer?
Yes, tritium exposure can increase cancer risk over time. Its beta radiation can damage DNA and cells, potentially leading to mutations. The risk depends on exposure level and duration. Minimizing tritium intake reduces this health hazard effectively.
Conclusion
Tritium poses risks to health and the environment. Exposure can harm cells and organs. Safe handling and disposal reduce dangers. Understanding these risks helps protect people and nature. Stay informed and cautious around tritium sources. Small steps make a big difference.
Keep safety first to avoid harm. Awareness is key to managing tritium safely.
Apply for this vacancy
For more information
For more information, please don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re here to assist with any questions or provide additional details to help you make informed decisions. Reach out today, and let’s connect!
Please mention the respective article number.
For more information
For more information, please don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re here to assist with any questions or provide additional details to help you make informed decisions. Reach out today, and let’s connect!
Please mention the respective article number.

