Are you curious about Tritium and how it affects your safety? Understanding Tritium radiation safety is crucial if you work with it or come across it in daily life.
You might wonder if it’s dangerous or how to protect yourself and others. This article will give you clear, simple answers and practical tips to keep you safe. Keep reading to discover what you need to know about Tritium radiation safety—your health depends on it.

Basics Of Tritium
Tritium is a radioactive form of hydrogen. It has unique properties that affect safety practices. Understanding tritium helps manage risks and protect health.
This section covers the basics of tritium. You will learn what tritium is and where it comes from. This knowledge is key to radiation safety.
What Is Tritium?
Tritium is a rare hydrogen isotope. It contains one proton and two neutrons. This makes it unstable and radioactive.
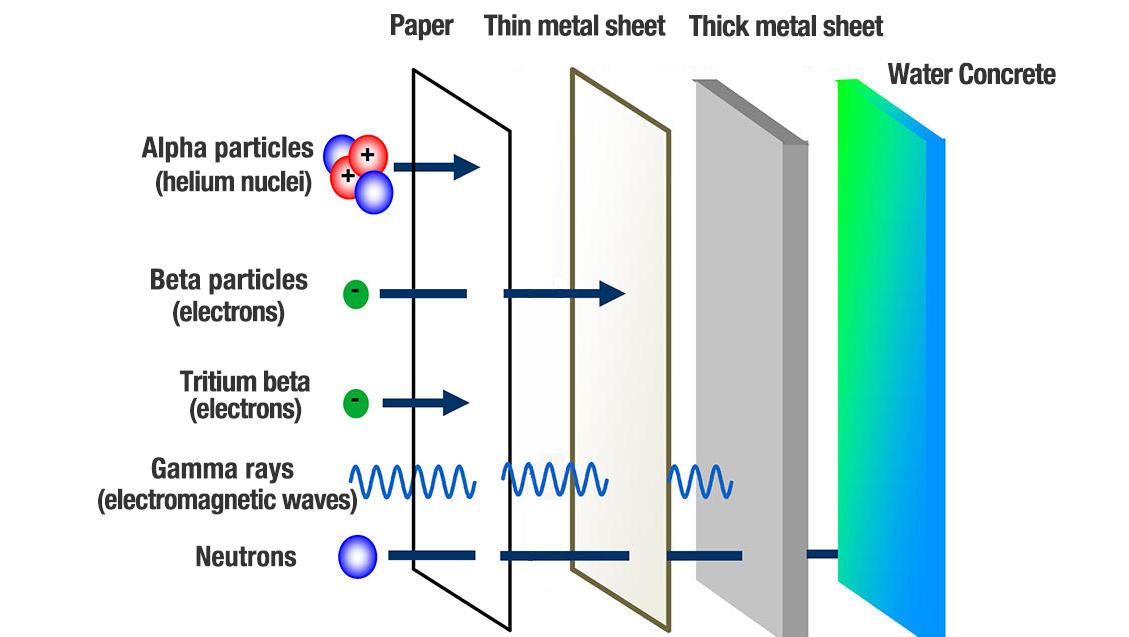
Tritium emits low-energy beta particles. These particles cannot penetrate the skin. But they can harm the body if tritium enters it.
Tritium occurs naturally in small amounts. It is also made in nuclear reactors. Its half-life is about 12 years.
Sources Of Tritium Exposure
Tritium exposure can come from several sources. Nuclear power plants release small amounts. Research labs and medical facilities use tritium too.
It can enter the body by breathing or drinking water. Tritium can also get in through skin wounds. Contaminated food may be another source.
Environmental tritium comes from the atmosphere and groundwater. Its levels are usually low but can vary near nuclear sites.
Health Risks Of Tritium
Tritium is a radioactive form of hydrogen. It occurs naturally but can also be produced in labs. Understanding its health risks helps keep people safe. Tritium emits low-energy radiation. This radiation can affect the human body in specific ways. Safety measures are important to reduce exposure.
Radiation Effects On The Body
Tritium emits beta particles. These particles cannot penetrate the skin deeply. The main risk comes from inhaling or ingesting tritium. Once inside, it spreads through body fluids. It can cause damage to cells and DNA. This damage may lead to health problems over time. The effects depend on the amount and length of exposure.
Long-term Exposure Concerns
Long-term exposure to tritium can increase health risks. It may cause changes in body tissues. Continuous exposure might raise the chance of cancer. Tritium’s low energy means risk is lower than other radiation. Still, safety guidelines limit how much people can be exposed to. Monitoring and control help prevent long-term harm.
Safe Handling Practices
Handling tritium safely requires clear and careful steps. This ensures protection from radiation risks. Safe handling limits exposure and keeps the environment secure. Understanding key practices is essential for anyone working with tritium.
Protective Gear Essentials
Wear gloves to avoid skin contact with tritium. Use lab coats to protect your clothes and skin. Safety goggles shield your eyes from accidental splashes. Masks prevent inhalation of tritium gases or vapors. Always check that protective gear fits well and is in good condition.
Proper Storage Methods
Store tritium in sealed containers to prevent leaks. Keep containers in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. Use clearly labeled storage areas to avoid confusion. Follow legal guidelines for storing radioactive materials. Regularly inspect storage for damage or leaks to maintain safety.
Detection And Monitoring
Detecting and monitoring tritium is crucial for safety. Tritium is a radioactive form of hydrogen. It can be hard to detect because it emits low-energy beta particles. Proper instruments and regular checks help keep environments safe. These tools measure tritium levels and alert workers to any hazards.
Instruments For Tritium Detection
Special instruments detect tritium in air, water, and surfaces. Liquid scintillation counters measure tritium in water samples. Ionization chambers and proportional counters detect airborne tritium. Handheld monitors help workers scan areas quickly. These devices ensure accurate, real-time readings. Choosing the right instrument depends on the situation and sensitivity needed.
Regular Safety Checks
Regular safety checks keep tritium exposure under control. Scheduled monitoring helps spot leaks or contamination early. Workers use detection tools to test air and surfaces. Records of these checks track safety over time. Immediate action follows if tritium levels rise above limits. Consistent checks protect health and maintain a safe workplace.
Emergency Response
Emergency response is critical for tritium radiation safety. Quick and careful actions reduce health risks and environmental damage. Tritium is a low-energy radioactive material but still requires proper handling during spills or leaks.
Every workplace with tritium must have a clear emergency plan. Training workers on these steps ensures a safe environment. Knowing how to act fast can prevent contamination and exposure.
Steps For Tritium Spills
First, alert everyone nearby about the spill. Avoid direct contact with the tritium. Evacuate the area if the spill is large or in a confined space.
Wear protective gloves and clothing before cleanup. Use absorbent materials like paper towels to contain the spill. Place the waste in a sealed, labeled container for disposal.
Notify the radiation safety officer immediately. Monitor the area for any remaining contamination using proper instruments. Follow all workplace safety protocols strictly.
Decontamination Procedures
Decontamination starts by removing contaminated clothing carefully. Wash exposed skin with mild soap and water. Avoid scrubbing hard to prevent skin damage.
Clean all tools and surfaces that touched tritium. Use specialized cleaning agents if available. Dispose of cleaning materials as radioactive waste.
Keep monitoring the area until no contamination is detected. Document the incident and cleanup steps for safety records. Regular training keeps everyone prepared for future emergencies.
Regulations And Guidelines
Understanding regulations and guidelines is key to safe handling of tritium radiation. These rules protect workers, the public, and the environment from harm. Strict standards guide how tritium is stored, used, and disposed of. Organizations follow these rules to reduce radiation risks effectively.
Government Safety Standards
Government agencies set clear safety standards for tritium use. These rules limit radiation exposure to safe levels. Agencies like the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) provide detailed guidelines. They cover everything from monitoring to emergency response. Compliance ensures public health and environmental protection.
Workplace Compliance
Workplaces handling tritium must follow strict safety rules. Employers train workers on radiation risks and protection methods. Regular checks and monitoring keep radiation levels low. Proper labeling and secure storage prevent accidents. Following these rules creates a safer work environment for all.
Reducing Exposure Risks
Reducing exposure risks to tritium radiation is vital for safety. Tritium emits low-energy beta particles that can be harmful with prolonged contact. Taking simple steps can lower the chance of exposure significantly. Understanding how to manage time and barriers helps protect against radiation.
Minimizing Contact Time
Spending less time near tritium sources reduces radiation exposure. Plan tasks carefully to finish quickly. Avoid unnecessary handling or staying close to the source. Shorter contact means less chance for radiation to affect the body.
Using Barriers Effectively
Barriers block or reduce radiation from tritium. Use materials like plastic, glass, or metal shields. Place barriers between you and the tritium source. Keep containers sealed and intact to prevent leaks. Proper barriers lower the risk of direct exposure.

Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Tritium And Why Is It Hazardous?
Tritium is a radioactive isotope of hydrogen. It emits low-energy beta radiation. Prolonged exposure may cause health risks like tissue damage. Proper handling and containment minimize hazards effectively.
How To Safely Handle Tritium In Laboratories?
Always use protective gloves and eyewear. Work in well-ventilated areas or fume hoods. Avoid inhaling or ingesting Tritium. Follow strict disposal protocols to prevent environmental contamination.
Can Tritium Radiation Penetrate The Skin?
No, Tritium’s beta radiation cannot penetrate human skin. However, internal exposure from ingestion or inhalation poses health risks. Avoid direct contact and ingestion for safety.
What Safety Measures Reduce Tritium Exposure Risk?
Use sealed containers and proper ventilation. Employ radiation detectors for monitoring levels. Implement strict safety training and emergency protocols. Regularly inspect equipment to prevent leaks.
Conclusion
Tritium radiation safety matters for health and the environment. Handle tritium with care to avoid exposure risks. Use proper tools and follow safety rules every time. Keep tritium away from food, water, and open wounds. Regular checks help find leaks or damage early.
Stay informed about tritium and share knowledge with others. Safe habits protect you and your community well. Small actions make a big difference in radiation safety.
Apply for this vacancy
For more information
For more information, please don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re here to assist with any questions or provide additional details to help you make informed decisions. Reach out today, and let’s connect!
Please mention the respective article number.
For more information
For more information, please don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re here to assist with any questions or provide additional details to help you make informed decisions. Reach out today, and let’s connect!
Please mention the respective article number.

