Have you ever wondered what powers the glowing lights on emergency exit signs or those tiny watch dials that shine in the dark? The secret often lies in something called tritium radiation.
It’s a fascinating and useful form of energy that quietly works behind the scenes in many everyday items you might not even notice. Understanding tritium radiation can help you see its benefits—and its risks—in a whole new light. Keep reading, and you’ll discover how this unique form of radiation impacts your world and why it matters to you.
Basics Of Tritium
Tritium is a rare form of hydrogen. It plays an important role in science and industry. Understanding its basics helps us learn about radiation and safety. Tritium has unique features that make it different from normal hydrogen. It emits a specific kind of radiation that is useful in many fields.
Properties And Sources
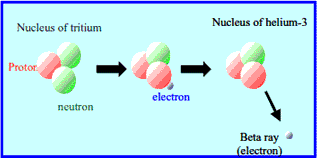
Tritium has one proton and two neutrons in its nucleus. This makes it heavier than normal hydrogen. It is radioactive and unstable. Tritium decays over time, turning into helium. It has a half-life of about 12 years. Natural sources include cosmic rays interacting with the atmosphere. Human activities like nuclear reactors also produce tritium. It can be found in small amounts in water and the environment.
How Tritium Emits Radiation
Tritium emits beta particles during decay. These are low-energy electrons. Beta particles cannot penetrate the skin deeply. They pose low risk outside the body but can be harmful if ingested. The radiation is weak and invisible. Special instruments detect tritium radiation. Its emission helps in scientific research and industrial applications like glow-in-the-dark devices.
Health Risks Linked To Tritium
Tritium is a radioactive form of hydrogen. It occurs naturally but is also made in nuclear reactors. People worry about its health risks because it can enter the body and affect cells. Understanding how tritium exposure happens helps protect health.
This section explains how tritium reaches the body and the possible effects it may cause. Clear knowledge helps reduce risks and stay safe around tritium sources.
Exposure Pathways
Tritium mainly enters the body through water. It can be in drinking water or food contaminated by tritium. Breathing air with tritium gas is less common but possible near nuclear sites. Skin contact with tritiated water may cause some absorption too. The body treats tritium like normal hydrogen, so it spreads quickly in tissues.
Potential Biological Effects
Tritium emits weak radiation called beta particles. These particles cause little damage outside the body but can harm cells inside. The radiation may change DNA and increase the chance of cancer. Effects depend on how much tritium enters and how long it stays in the body. Most tritium leaves the body within days, lowering long-term risks.
Environmental Impact
Tritium radiation affects the environment in several ways. It is a radioactive form of hydrogen found naturally and from human activities. Understanding its impact is important for safety and health.
Tritium can enter water and air, spreading through ecosystems. Its presence raises concerns about long-term effects on plants, animals, and humans. Careful monitoring and control help reduce risks.
Tritium In Water And Air
Tritium often appears in water as tritiated water. This water mixes with lakes, rivers, and groundwater. Plants and animals absorb it easily.
In air, tritium exists as a gas or part of water vapor. It can travel long distances with the wind. This movement increases the chance of exposure far from the source.
Water contamination is a major concern. People and wildlife may drink or come into contact with tritium-contaminated water. This can lead to internal radiation exposure.
Long-term Ecological Concerns
Tritium’s low energy makes it less dangerous than other radiation. Yet, long-term exposure can affect cell DNA. This can cause mutations or health issues in wildlife.
Soil and plants can store tritium, passing it through the food chain. Over time, this build-up may harm ecosystems. Some species could face changes in growth or reproduction.
Monitoring tritium levels helps protect the environment. Scientists study its movement and effects to create safe limits. This protects future generations of plants, animals, and humans.
Measuring Tritium Levels
Measuring tritium levels is important for safety and environmental health. Tritium is a radioactive form of hydrogen. It can be found in water, air, and soil near nuclear sites. Accurate measurement helps monitor exposure and control contamination. Scientists use special tools and methods to detect tritium effectively.
Detection Techniques
Liquid scintillation counting is a common method. It detects the weak radiation tritium emits. Water samples mix with a scintillation fluid that glows when radiation hits it. The light is measured by a detector to find tritium levels.
Another method is gas proportional counting. This technique uses a gas-filled chamber to detect radiation particles. It is useful for solid samples or gas forms of tritium. Both methods are sensitive and provide reliable results.
Regulatory Limits
Governments set strict limits on tritium levels to protect health. These limits vary by country but are usually very low. For drinking water, the limit is often in the range of a few thousand picocuries per liter.
Regular monitoring ensures these limits are not exceeded. If tritium levels rise above safe limits, action is taken to reduce exposure. These rules help keep communities and environments safe from radiation risks.
Safety Measures In Tritium Handling
Handling tritium requires strict safety measures to protect workers and the environment. Tritium is a radioactive form of hydrogen, and exposure can be harmful. Following safety rules reduces risks and keeps everyone safe.
Proper safety gear and clear workplace rules are key to safe tritium handling. Workers must understand and apply these measures every day. Careful control helps prevent accidents and contamination.
Protective Equipment
Workers must wear special protective clothing to avoid skin contact. Gloves and lab coats made from materials that block tritium help reduce exposure. Safety goggles protect the eyes from any splashes or vapors.
Respirators may be needed when working with tritium gas or liquids. These devices filter out harmful particles and gases. Using the right equipment prevents tritium from entering the body.
Workplace Protocols
Strict rules guide how to handle and store tritium safely. Work areas must have proper ventilation to clear any released gas. Regular monitoring checks air and surfaces for tritium contamination.
Spills must be cleaned immediately using approved methods. Waste is stored in sealed containers and disposed of carefully. Training workers on these protocols ensures safety and reduces risk.

Tritium Use In Industry
Tritium is a radioactive form of hydrogen used widely in several industries. Its unique properties make it valuable for many industrial processes. Understanding how tritium is used helps us see its role in modern technology and science.
Applications In Energy And Research
Tritium plays a key role in energy, especially in nuclear fusion research. Scientists use tritium as fuel in experimental reactors. It helps create energy by fusing atomic nuclei. This process could one day provide clean power.
Besides energy, tritium is used in research labs. It acts as a tracer to study chemical and biological processes. Researchers track movement of molecules with tritium labels. This helps in drug development and environmental studies.
Safety Practices In Industry
Handling tritium requires strict safety rules. Workers use protective gear to avoid exposure. Facilities have special ventilation to control air quality.
Regular monitoring detects any leaks or spills early. Companies follow guidelines from health authorities. These measures keep employees and the environment safe from radiation risks.
Future Of Tritium Safety
The future of tritium safety focuses on protecting people and the environment. Tritium is a weak radioactive element. It needs careful handling to prevent harm. Scientists and regulators work hard to improve safety standards. They use new tools and rules to reduce risks. These efforts aim for safer use of tritium in industries and research.
Advances In Monitoring
New technology helps detect tritium faster and more accurately. Sensors can now measure very low levels of radiation. This allows early warning of any leaks or spills. Continuous monitoring systems track tritium in air and water. Data from these systems help prevent exposure to harmful radiation. Improved monitoring protects workers and nearby communities. It also supports quick response to accidents.
Emerging Regulations
Governments are updating rules to better control tritium use. New limits on emissions help reduce environmental impact. Regulations require strict safety plans for handling tritium. Facilities must report tritium levels regularly to authorities. Training programs for workers are becoming mandatory. These laws aim to keep public health safe. They encourage safer methods and better equipment for tritium work.

Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Tritium Radiation And Where Does It Come From?
Tritium radiation is a low-energy beta radiation emitted by tritium, a radioactive hydrogen isotope. It naturally occurs in the atmosphere and is also produced in nuclear reactors and weapons.
Is Tritium Radiation Harmful To Human Health?
Tritium radiation is low-energy and cannot penetrate skin. However, ingestion or inhalation of tritium-contaminated water or air may pose health risks, requiring safety precautions.
How Is Tritium Radiation Detected And Measured?
Tritium radiation is detected using liquid scintillation counters or gas proportional counters. These devices measure beta particles emitted by tritium for accurate quantification.
What Are Common Uses Of Tritium Radiation?
Tritium radiation is used in self-luminous devices like exit signs, watch dials, and gun sights. Its glow does not require external power sources.
Conclusion
Tritium radiation plays a key role in science and industry. It has unique uses that help many fields grow. People should learn how to handle it safely. Understanding its risks and benefits is very important. Careful use keeps people and the environment protected.
Tritium will stay important in the future of technology. Knowing the basics helps everyone stay informed and safe. Simple steps make a big difference in handling tritium. Stay aware and respect its power for best results.
Apply for this vacancy
For more information
For more information, please don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re here to assist with any questions or provide additional details to help you make informed decisions. Reach out today, and let’s connect!
Please mention the respective article number.
For more information
For more information, please don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re here to assist with any questions or provide additional details to help you make informed decisions. Reach out today, and let’s connect!
Please mention the respective article number.

