Have you ever wondered what makes certain glow-in-the-dark watches shine without batteries? Or how some emergency exit signs stay lit for years without any power source?
The secret lies in a fascinating substance called the Tritium element. Understanding Tritium can change the way you see everyday objects and even reveal its surprising uses in science and technology. If you’re curious about this unique element and how it impacts your life, keep reading—because what you’ll discover might just light up your world in more ways than one.
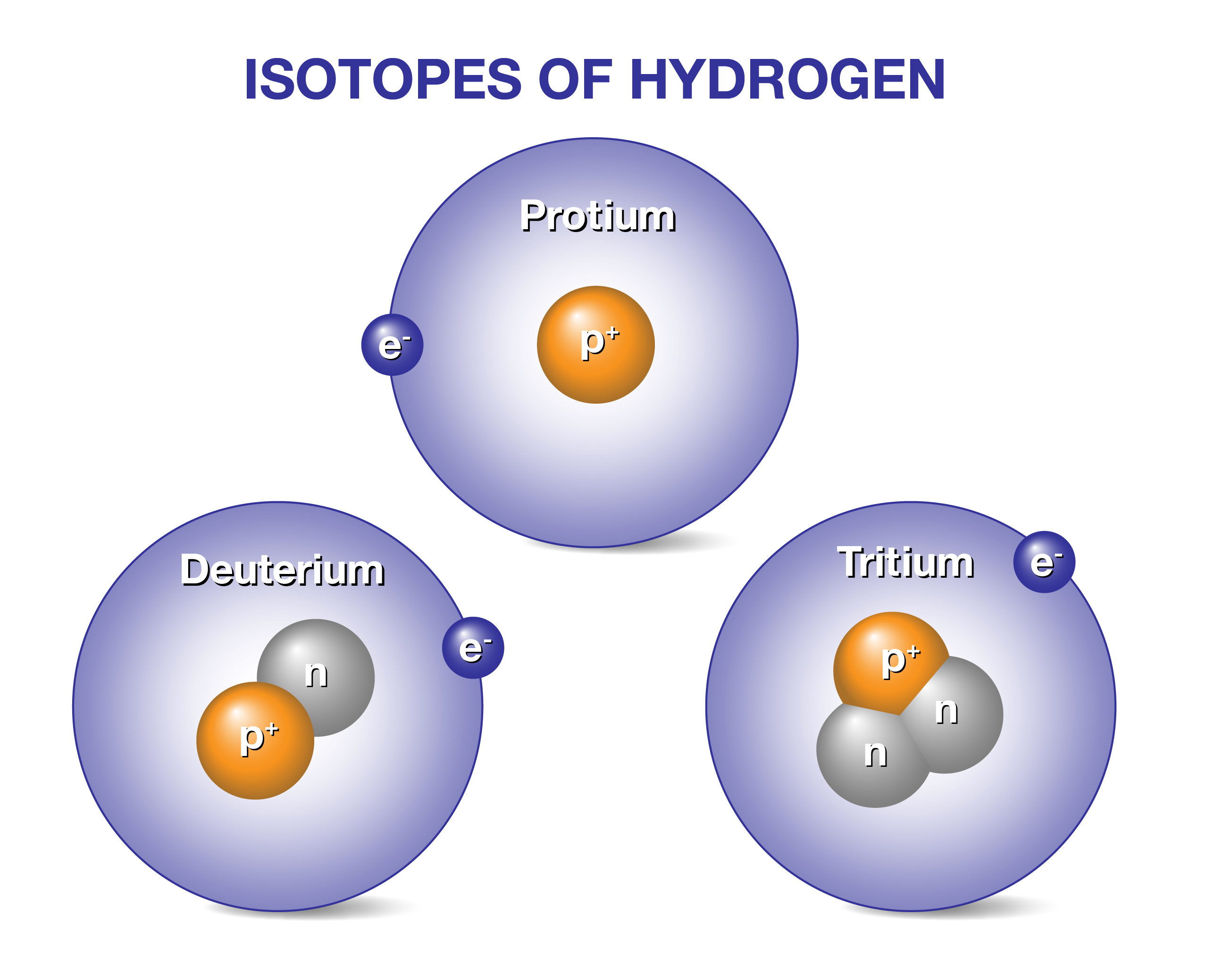
Tritium Basics
Tritium is a rare form of hydrogen. It has unique features that make it interesting. This section explains the basics of tritium. You will learn about its structure, where it is found, and its special properties.
Atomic Structure
Tritium is a hydrogen isotope. It has one proton in its nucleus. It also has two neutrons. This is different from normal hydrogen, which has none. Its atomic number is 1, like all hydrogen atoms. The extra neutrons make tritium heavier.
Natural Occurrence
Tritium is very rare in nature. It forms when cosmic rays hit the Earth’s atmosphere. This creates small amounts of tritium gas. It also appears in trace amounts in water. Most tritium on Earth is man-made. It is produced in nuclear reactors and weapons tests.
Radioactive Properties
Tritium is radioactive. It emits low-energy beta particles. These particles cannot penetrate human skin. It has a half-life of about 12.3 years. This means half of it decays in that time. Its radiation makes tritium useful for special applications.
Production Methods
Tritium is a rare and valuable element. It forms naturally in small amounts but is mostly made through special processes. Understanding how tritium is produced helps us see its uses in science and industry.
Different methods create tritium, each with its own tools and conditions. These methods include using nuclear reactors, particle accelerators, and natural cosmic rays. Each process affects the amount and purity of tritium produced.
Nuclear Reactors
Nuclear reactors produce most of the tritium used today. Inside reactors, lithium or heavy water captures neutrons. This reaction turns lithium or deuterium into tritium. The process is controlled to keep tritium safe and pure. Reactors provide a steady tritium supply for research and industry.
Particle Accelerators
Particle accelerators create tritium by smashing particles at high speeds. Protons or deuterons hit targets like lithium or boron. This collision produces tritium atoms among other particles. The method allows precise control over production. It is useful for experiments and small-scale tritium needs.
Cosmic Ray Interactions
Cosmic rays constantly hit the Earth’s atmosphere. These high-energy particles cause reactions in nitrogen and oxygen. One result is the natural creation of small tritium amounts. This tritium slowly falls to Earth’s surface in rain. The natural process is slow and produces limited tritium.
Energy Applications
Tritium plays a unique role in energy applications. Its special properties make it useful in several areas. These include fusion energy, lighting, and military uses. Each use shows how tritium supports energy needs in different ways.
Understanding these applications helps us see tritium’s importance. It also shows how science uses this rare element for practical energy solutions.
Fusion Fuel Potential
Tritium is a key fuel for fusion reactors. Fusion is the process that powers the sun. Scientists try to copy this process to create clean energy. Tritium combines with deuterium to release huge energy. This reaction produces more energy than it consumes. Using tritium could lead to safe and powerful energy sources. Research continues to make fusion energy practical.
Self-powered Lighting
Tritium helps make self-powered lights. It glows without electricity or batteries. These lights use tritium gas inside glass tubes. The gas emits light through a process called radioluminescence. This makes tritium useful in exit signs and watches. The light lasts for many years without fading. It is safe and reliable for low-light conditions.
Nuclear Weapons
Tritium is used in some nuclear weapons. It increases the weapon’s power by boosting the nuclear reaction. Tritium must be regularly replaced because it decays over time. This element is controlled and monitored strictly worldwide. Its use in weapons shows the dual nature of tritium. It can be used for energy or military purposes.
Medical Uses
Tritium is a rare form of hydrogen with unique medical uses. Its radioactive nature helps in several health fields. Tritium’s ability to emit low-energy radiation makes it useful and safe for many treatments and tests.
This section explains how tritium is used in medicine. It covers radiolabeling, diagnostic tools, and cancer treatment.
Radiolabeling
Tritium helps scientists track molecules inside the body. It attaches to drugs or chemicals without changing them. This process, called radiolabeling, shows how medicines move and work. Researchers learn about drug absorption and metabolism. It improves drug design and safety tests.
Diagnostic Tools
Tritium is part of some diagnostic tools. It helps detect diseases by marking substances in the body. These markers emit signals that machines can read. Doctors use these signals to see inside tissues and organs. Tritium’s low radiation reduces risks for patients. It provides clear images for accurate diagnoses.
Cancer Treatment
Tritium plays a role in cancer treatment. It is used in targeted therapies to kill cancer cells. Its radiation damages cancer DNA, stopping growth. Tritium’s low energy limits harm to healthy cells. This makes treatments safer and more focused. Research continues to improve tritium-based therapies.
Industrial And Commercial Uses
Tritium is a rare form of hydrogen with unique properties. It plays a key role in many industries. Its ability to glow without electricity makes it useful in different fields. Tritium’s radioactive nature helps in tracing and safety applications. These features make it valuable in industrial and commercial uses.
Glow-in-the-dark Devices
Tritium is widely used in glow-in-the-dark devices. It powers self-illuminating watches and exit signs. These devices do not need batteries or external light. Tritium gas lights shine continuously for years. They provide visibility in dark or emergency situations. This makes them ideal for safety and convenience.
Safety Equipment
Tritium improves safety equipment performance. It is found in emergency exit signs and gun sights. The glowing effect helps people see clearly in low light. Tritium lights work well in harsh environments. They are reliable during power failures and disasters. This reliability enhances safety in homes and workplaces.
Environmental Tracing
Scientists use tritium for environmental tracing. It helps track water movement in rivers and oceans. Tritium’s radioactivity acts as a natural marker. This tracing helps study pollution and water cycles. It supports better environmental management and protection. Tritium provides important data for scientists worldwide.
Safety And Environmental Impact
Tritium is a radioactive form of hydrogen used in various fields. Safety and environmental impact are key concerns for its use. Understanding these factors helps manage risks and protect the environment.
This section explores radiation risks, containment measures, and disposal challenges related to tritium.
Radiation Risks
Tritium emits low-energy beta radiation. This radiation cannot penetrate human skin. The main risk comes from ingesting or inhaling tritium. Inside the body, it can damage cells and DNA. Long-term exposure may increase cancer risk. Careful handling reduces these dangers.
Containment Measures
Tritium must be stored in sealed containers to prevent leaks. Facilities use special barriers and ventilation systems. Monitoring devices detect any release early. Workers follow strict safety protocols. These steps limit exposure and protect health.
Disposal Challenges
Tritium disposal is difficult due to its radioactivity and long half-life. It cannot be destroyed easily. Safe storage in secure sites is required. Environmental release must be avoided to protect water and soil. Research continues to find better disposal methods.
Future Prospects
The future of tritium holds great potential for science and industry. This rare hydrogen isotope plays a vital role in energy and technology. As research grows, new uses and challenges come into view.
Understanding tritium’s future helps us prepare for cleaner energy and smarter applications. It also raises questions about safety and supply that need careful attention.
Advances In Fusion Research
Tritium is key to nuclear fusion, a clean energy source. Scientists study fusion to create power without pollution. New experiments aim to use tritium and deuterium to start fusion reactions. Success could lead to abundant, safe energy for the world.
Research focuses on improving tritium handling and fuel efficiency. Better technology means fusion reactors might work faster and last longer. This progress brings us closer to practical fusion power plants.
Innovative Applications
Tritium finds use in many fields beyond energy. It helps make glowing watch dials and emergency exit signs. Medical tools use tritium to track chemical processes. Scientists also explore its use in sensors and self-powered devices.
New ideas include tritium in space missions and environmental monitoring. These uses show how versatile this element can be. Innovation will likely reveal more practical uses in coming years.
Sustainability Concerns
Tritium’s radioactive nature requires careful management. Its production and disposal raise environmental questions. Safe storage and recycling methods are crucial to reduce risks.
Supply limits of tritium challenge its long-term use. Researchers look for ways to produce tritium more sustainably. Balancing benefits with safety and resource care remains a priority.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Tritium And Its Basic Properties?
Tritium is a radioactive isotope of hydrogen with one proton and two neutrons. It emits low-energy beta radiation and has a half-life of about 12. 3 years. Tritium is rare in nature but can be artificially produced in nuclear reactors.
How Is Tritium Used In Practical Applications?
Tritium is used in self-luminous devices like watch dials and exit signs. It also serves as a tracer in biochemical research and as fuel in nuclear fusion reactions. Its glowing property makes it valuable for low-light visibility.
Is Tritium Safe For Human Exposure?
Tritium emits weak beta particles, which cannot penetrate the skin. However, ingestion or inhalation of tritium-contaminated water or air can pose health risks. Proper handling and safety measures minimize exposure and ensure safe use.
How Is Tritium Produced Industrially?
Tritium is mainly produced by neutron bombardment of lithium-6 in nuclear reactors. It can also be generated during nuclear weapons testing and certain nuclear reactions. Industrial production is controlled due to its radioactive nature.
Conclusion
Tritium is a rare and useful element with unique features. It plays a key role in science and technology. People use it in medicine, energy, and safety tools. Understanding tritium helps us learn about the world better. Its future uses might grow with new research.
Tritium’s importance is clear and will likely continue. Small but powerful, it shows how elements impact daily life. Keep exploring to see how tritium shapes tomorrow.
Apply for this vacancy
For more information
For more information, please don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re here to assist with any questions or provide additional details to help you make informed decisions. Reach out today, and let’s connect!
Please mention the respective article number.
For more information
For more information, please don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re here to assist with any questions or provide additional details to help you make informed decisions. Reach out today, and let’s connect!
Please mention the respective article number.

