Are you curious about Tritium and want a clear, simple guide that answers all your questions? Whether you’ve heard the name before or are just discovering it, this Tritium Wiki will give you everything you need to know.
From what Tritium is to how it works and why it matters, you’ll find easy explanations that make complex ideas feel straightforward. Keep reading to unlock the facts and insights that can help you understand Tritium like a pro.
Basics Of Tritium
Tritium is a rare form of hydrogen with unique features. It plays a key role in science and technology. Understanding tritium helps explain its uses and risks.
This section covers the basics of tritium. Learn what it is, its physical traits, and where it naturally appears.
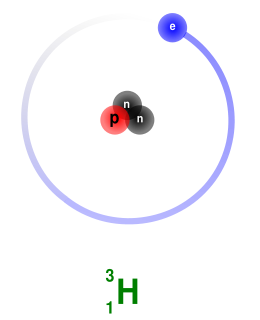
What Is Tritium
Tritium is a hydrogen isotope. It has one proton and two neutrons. This makes it heavier than normal hydrogen. Tritium is radioactive. It emits weak radiation and decays over time. Scientists use tritium in research and industry.
Physical Properties
Tritium is a gas at room temperature. It behaves like normal hydrogen gas. Its color is invisible, and it has no smell. Tritium glows faintly in the dark due to radiation. It combines with oxygen to form tritiated water. This water is chemically similar to regular water.
Natural Occurrence
Tritium forms naturally in the upper atmosphere. Cosmic rays hit nitrogen atoms and create tritium. It falls to Earth with rain and snow. Tritium also appears in small amounts in groundwater. Human activities like nuclear tests increase tritium levels.
Production Methods
Tritium is a rare and valuable isotope used in various fields. Producing tritium requires specific methods. These methods ensure a steady supply for industry and research. Understanding these production techniques helps grasp how tritium is made and used.
Nuclear Reactors
Nuclear reactors produce tritium through neutron reactions. Heavy water reactors use deuterium to capture neutrons. This reaction forms tritium as a byproduct. Tritium is then extracted from the reactor’s coolant or moderator. This method provides a reliable source of tritium for many applications.
Particle Accelerators
Particle accelerators create tritium by bombarding targets with high-energy particles. Protons or deuterons hit lithium or boron targets. This causes nuclear reactions that generate tritium atoms. Accelerators offer a controlled way to produce tritium in smaller amounts. This method suits research facilities and specialized uses.
Other Techniques
Other less common methods also exist for tritium production. These include nuclear fusion experiments and certain chemical reactions. Fusion reactors can produce tritium as part of their fuel cycle. Some chemical processes extract tritium from natural sources. These techniques are still developing and less widespread.
Energy Potential
Tritium holds a unique place in energy science. It is a rare form of hydrogen with special properties. Its energy potential is important for many fields, especially nuclear energy. Understanding how tritium works helps us see its true value.
Exploring tritium’s energy potential means looking at its radioactive nature, role in fusion, and energy efficiency. These factors show why tritium attracts attention worldwide.
Radioactive Decay
Tritium is radioactive. It slowly breaks down over time. This process releases energy in the form of low-energy beta particles. The decay happens naturally and is measured in years. This slow decay makes tritium safe for certain uses. It provides a steady energy source without sudden bursts.
Fusion Fuel Role
Tritium is key for nuclear fusion. Fusion is the process that powers the sun. It joins light atoms to release large energy. Tritium combines with deuterium in fusion reactors. This fusion creates huge energy output. Scientists study tritium to develop clean energy sources. Its ability to fuel fusion is a major advantage.
Energy Efficiency
Tritium has high energy efficiency. A small amount produces a lot of energy. Its efficiency is better than many fuels today. This means less fuel is needed for more power. Efficient energy use helps reduce waste and cost. Tritium’s efficiency makes it promising for future energy needs.
Common Applications
Tritium is a special material used in many ways. It glows without needing batteries or power. This makes it very useful in different fields. Below are some common uses of tritium in everyday life and industry.
Self-powered Lighting
Tritium is often used in self-powered lighting. It lights up watch dials and exit signs. The glow lasts for years without any electricity. This makes places safer during power outages. It also appears in keychains and firearm sights.
Medical Uses
In medicine, tritium helps in tracing and imaging. It is used to label molecules in tests. Doctors track how drugs move in the body. This helps to understand diseases better. Tritium’s low radiation is safe for these uses.
Industrial Uses
Industries use tritium in various tools and devices. It helps measure pressure and temperature in harsh places. Tritium lights are used in aircraft and ships for visibility. It also assists in scientific research and experiments.
Tritium In Fusion Research
Tritium is a key fuel in fusion research. It helps scientists create energy like the sun. Fusion has the potential to provide clean and almost limitless power. Tritium’s role is important because it reacts easily with deuterium to release energy.
Researchers study tritium to improve fusion reactor designs and solve many challenges. Understanding tritium behavior helps make fusion energy safer and more efficient. This section explores its use in fusion research.
Fusion Reactor Designs
Many fusion reactor designs use tritium as fuel. Tokamaks are the most common. They use magnetic fields to hold hot plasma. Inside the plasma, tritium and deuterium fuse and create energy.
Another design is the inertial confinement reactor. It uses lasers to heat and compress fuel pellets containing tritium. Both designs aim to maintain stable conditions for fusion to happen.
Challenges In Fusion
Handling tritium is difficult. It is radioactive and can escape easily. Safe storage and containment are critical. Fusion reactors also need a steady tritium supply, which is hard to produce.
Fusion reactions create high temperatures and radiation. These conditions damage reactor materials. Scientists work on materials that resist this damage. Controlling plasma to keep fusion steady is another challenge.
Future Prospects
Research continues to improve tritium use in fusion. New methods aim to breed more tritium inside reactors. This could reduce fuel shortages.
Advanced reactor designs may increase energy output and safety. Fusion power plants might become a clean energy source worldwide. Tritium remains a central part of this journey.
Safety And Environmental Impact
Tritium is a radioactive form of hydrogen used in various industries. Understanding its safety and environmental impact is important. This section explains the risks, how to handle it safely, and proper waste management.
Radiation Risks
Tritium emits low-energy beta radiation. It cannot penetrate the skin. The main danger is swallowing or inhaling it. Inside the body, it can affect cells and tissues. Prolonged exposure may increase health risks. Safe limits for tritium exposure are strictly set by authorities. Monitoring and controlling exposure helps protect workers and the public.
Handling Precautions
Handling tritium requires care and safety equipment. Workers use gloves and protective clothing. Special ventilation systems reduce inhalation risks. Containers must be sealed tightly to avoid leaks. Regular training helps staff follow safety rules. Proper labeling and storage prevent accidents. Emergency plans prepare for spills or exposure.
Waste Management
Tritium waste must be managed carefully to protect the environment. It is often stored until its radioactivity decreases. Secure containers prevent leaks into soil and water. Disposal follows strict government regulations. Recycling some tritium materials is possible in certain cases. Tracking waste ensures no harmful release occurs. Safe waste management reduces environmental impact.
Regulations And Policies
Regulations and policies guide the safe use and handling of tritium. They help protect people and the environment. These rules vary worldwide but share common goals. Understanding these rules is key for anyone working with tritium.
International Guidelines
International agencies set rules for tritium use. The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) provides safety standards. These standards cover radiation protection and waste management. Countries follow these guidelines to ensure safety and consistency.
National Regulations
Each country has its own laws about tritium. These laws control production, use, and disposal. Agencies monitor tritium to prevent misuse and accidents. Compliance with these rules is mandatory for businesses and labs.
Transport And Storage
Transporting tritium requires strict safety measures. Containers must prevent leaks and radiation exposure. Storage facilities need secure and controlled environments. These practices reduce risks during movement and storage.

Innovations And Future Trends
The world of tritium is evolving fast. Innovations and future trends show how this element will shape many industries. New methods and ideas improve how tritium is made and used. These advances promise safer, greener, and more effective solutions.
Advanced Production Techniques
Scientists develop smarter ways to produce tritium. These methods use less energy and create fewer wastes. New technology helps capture tritium more efficiently. This reduces costs and increases availability for different uses.
Emerging Applications
Tritium finds new roles beyond traditional uses. It supports medical devices that need precise timing. In clean energy, tritium powers fusion research. It also plays a part in advanced lighting and security systems.
Sustainability Efforts
Efforts focus on making tritium use safer for the planet. Recycling tritium lowers the need for fresh production. Researchers work on reducing environmental impact. This ensures tritium helps without harming nature or people.

Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Tritium And How Does It Work?
Tritium is a radioactive isotope of hydrogen used in self-luminous devices. It emits low-energy beta particles that excite phosphor, creating light without external power. Tritium is safe in sealed containers and is commonly used in watches, exit signs, and instruments for continuous illumination.
Where Is Tritium Commonly Used Today?
Tritium is mainly used in watch dials, exit signs, and military instruments. It provides constant glow without batteries or electricity. Its long half-life makes it ideal for emergency lighting and scientific applications requiring reliable, low-level illumination in dark environments.
Is Tritium Safe For Humans And The Environment?
Tritium is generally safe when contained properly. Its beta radiation cannot penetrate skin, but ingestion or inhalation is harmful. Used in sealed devices, it poses minimal risk. Environmental concerns focus on potential leaks, but strict regulations control its handling and disposal to ensure safety.
How Is Tritium Produced For Industrial Use?
Tritium is produced in nuclear reactors by bombarding lithium or heavy water with neutrons. This process creates tritium atoms that are then collected and purified. Industrial Tritium supply is controlled due to its radioactive nature and is primarily managed by government and authorized facilities.
Conclusion
Tritium is a unique element with many uses. It glows without needing power. People use it in watches, signs, and tools. Its safe handling is very important. Knowing about Tritium helps us understand science better. This wiki gives clear facts about Tritium.
Keep learning to see how it affects daily life. Simple yet fascinating. Tritium’s role in technology and nature is worth exploring.
Apply for this vacancy
For more information
For more information, please don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re here to assist with any questions or provide additional details to help you make informed decisions. Reach out today, and let’s connect!
Please mention the respective article number.
For more information
For more information, please don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re here to assist with any questions or provide additional details to help you make informed decisions. Reach out today, and let’s connect!
Please mention the respective article number.

