Have you ever wondered how something as rare and powerful as tritium is made? Tritium plays a key role in many important technologies, from glowing watch dials to advanced energy research.
But what exactly goes into creating this special form of hydrogen? Understanding how tritium is made can open your eyes to the science behind cutting-edge innovations. Keep reading, and you’ll discover the fascinating process that brings tritium to life—and why it matters for your world.
Tritium Basics
Tritium is a rare form of hydrogen. It plays an important role in science and technology. Understanding its basics helps us see how it is made and used. Tritium has unique traits that make it special. These traits affect how it behaves and interacts with other elements.
This section explains what tritium is and its unique properties. It gives a clear idea of why tritium matters in many fields.
What Is Tritium
Tritium is a hydrogen isotope. It contains one proton and two neutrons in its nucleus. This makes it heavier than normal hydrogen. Tritium is radioactive and slowly breaks down over time. It is rare in nature and mostly made in labs.
Scientists use tritium in nuclear fusion and glow-in-the-dark devices. It appears naturally in small amounts from cosmic rays hitting the atmosphere.
Unique Properties
Tritium emits low-energy beta particles. These particles can make materials glow without heat or light. It has a half-life of about 12 years. This means half of it decays in that time. Tritium’s radioactivity is weak and usually safe in small amounts.
Its ability to glow makes it useful in watches, signs, and instruments. Tritium’s weight and radioactivity also help in scientific research and energy production.
Natural Occurrence
Tritium forms naturally when cosmic rays hit the Earth’s atmosphere. This process creates a small amount of tritium that mixes with air and water. It is rare but constantly produced in nature.
Sources In The Environment
Tritium exists naturally in small amounts on Earth. It is not common but can be found in the atmosphere, oceans, and soil. This rare hydrogen isotope forms through natural processes. It slowly spreads and mixes with water and air around us. Natural tritium is always present but in very low levels.
Cosmic Ray Interaction
Cosmic rays from space hit Earth’s atmosphere constantly. These high-energy particles cause nuclear reactions in the air. When cosmic rays collide with nitrogen atoms, tritium is produced. This process creates tritium in the upper atmosphere. The tritium then falls to Earth with rain and snow. This natural creation keeps tritium levels steady over time.
Artificial Production Methods
Artificial production methods create tritium in labs and facilities. These methods use advanced technology to produce tritium safely and efficiently. Tritium is rare in nature, so artificial production is important. Three main methods produce tritium: nuclear reactors, particle accelerators, and neutron activation. Each method uses a different scientific process to generate this valuable isotope.
Nuclear Reactors
Nuclear reactors create tritium through nuclear reactions. Heavy water reactors use deuterium in water. Neutrons hit deuterium atoms, turning them into tritium. Some reactors add lithium rods. Neutrons collide with lithium, producing tritium and helium. This method produces large amounts of tritium. It is widely used for commercial and research purposes.
Particle Accelerators
Particle accelerators smash particles at high speed. They shoot protons into targets made of lithium or other materials. The collision creates tritium atoms. Accelerators can control the process precisely. This method produces tritium quickly in small amounts. It is useful for experiments and special applications.
Neutron Activation
Neutron activation uses neutrons to change atomic nuclei. Materials like lithium or boron absorb neutrons in a reactor. The absorption transforms them into tritium. This method is efficient for producing tritium in small batches. It also helps monitor neutron flow in reactors. Neutron activation is a reliable way to generate tritium safely.
Role Of Heavy Water Reactors
Heavy water reactors play a key role in producing tritium. Tritium is a rare hydrogen isotope used in various fields, including nuclear energy and medicine. These reactors use heavy water as a moderator to slow down neutrons. Slower neutrons help sustain nuclear reactions more efficiently.
Heavy water reactors can produce tritium by exposing lithium or deuterium targets to neutron radiation. The design of these reactors allows for better neutron economy, which increases tritium yield. This makes them important tools for tritium production worldwide.
How Heavy Water Boosts Production
Heavy water, or D2O, contains deuterium instead of normal hydrogen. It absorbs fewer neutrons than regular water. This means more neutrons remain available to cause reactions that create tritium. The high neutron availability improves tritium production rates.
In addition, heavy water reactors can run using natural uranium fuel. This lowers the cost and complexity of operation. The long neutron life and high neutron flux in these reactors help produce tritium efficiently.
Common Reactor Types
Several types of heavy water reactors exist. The most common are the CANDU (Canada Deuterium Uranium) reactors. They are widely used for tritium production due to their efficient design.
Other heavy water reactors include the Indian PHWR (Pressurized Heavy Water Reactor). These reactors also produce tritium alongside electricity. Their ability to use natural uranium fuel makes them practical for many countries.
Extraction And Separation Techniques
Extracting and separating tritium requires precise and effective techniques. These methods isolate tritium from other gases and materials. The goal is to obtain pure tritium for use in scientific and industrial applications. Understanding these techniques helps explain how tritium is made and handled safely.
Gas Chromatography
Gas chromatography separates gases based on their properties. Tritium, mixed with other gases, passes through a column. Different gases move at different speeds in the column. This difference helps separate tritium from other components. The process is fast and accurate. It allows scientists to collect tritium in a pure form.
Cryogenic Distillation
Cryogenic distillation uses very low temperatures to separate gases. Tritium and other gases are cooled until they liquefy. Each gas liquefies at a different temperature. This difference lets tritium be separated from the rest. The liquid tritium is then collected for further use. This method is effective for large-scale tritium extraction.
Safety And Handling
Handling tritium requires strict safety measures. It is a radioactive substance with special risks. Workers must follow careful steps to avoid harm.
Radioactive Risks
Tritium emits low-energy beta radiation. This radiation cannot penetrate skin deeply. The main danger is inhaling or swallowing tritium. Inside the body, it can damage cells. Long exposure may increase cancer risk. Protecting workers from exposure is critical.
Containment Protocols
Tritium is stored in sealed containers. These containers prevent leaks and spills. Facilities use ventilation systems to control air quality. Workers wear protective gear like gloves and masks. Regular monitoring checks radiation levels in the air. Strict rules guide how to handle and dispose of tritium safely. These steps keep people and the environment safe.
Applications Of Tritium
Tritium is a rare and useful form of hydrogen. It has several important uses in science and industry. Its unique properties make it valuable in different fields. Below are some key applications of tritium.
Nuclear Fusion
Tritium plays a vital role in nuclear fusion research. It helps scientists create energy like the sun. Fusion combines tritium with deuterium to release large amounts of energy. This process could lead to clean and powerful energy sources in the future.
Self-powered Lighting
Tritium is used in self-powered lighting devices. It glows without electricity or batteries. This makes it useful for emergency exit signs, watch dials, and gun sights. The glow lasts many years, providing reliable light in dark places.
Medical Uses
In medicine, tritium helps track chemicals inside the body. It is used in radiolabeling to study how drugs work. This helps doctors develop better medicines and treatments. Tritium’s safe radiation levels make it suitable for these tests.
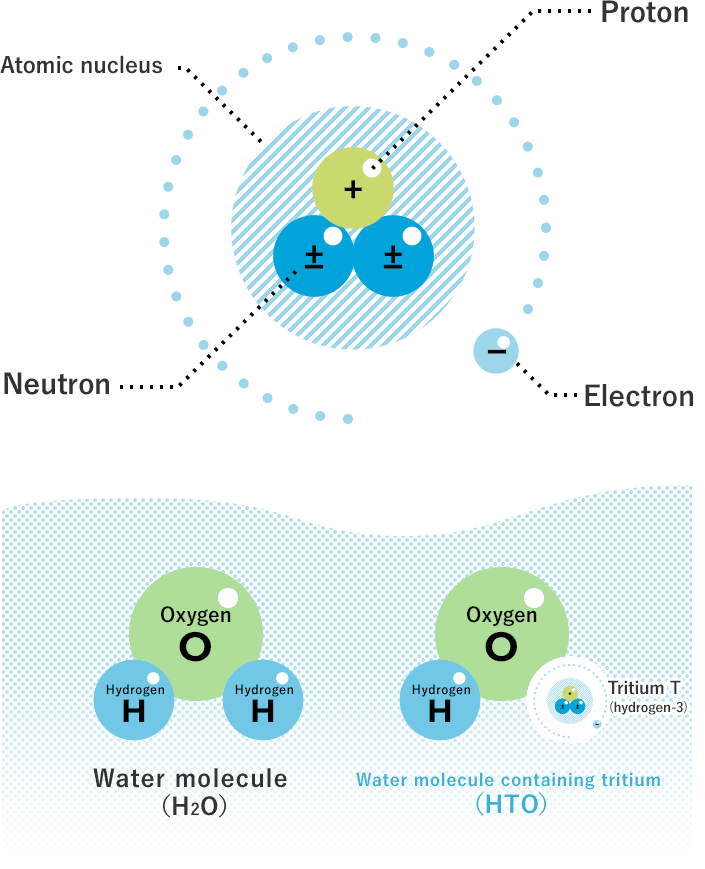
Future Production Trends
The future of tritium production shows many changes. New methods aim to make tritium more available and safer. Scientists focus on cutting costs and reducing waste. This shift will support energy and medical uses worldwide.
Advanced Reactor Designs
New reactor types promise higher tritium output. They use materials that produce tritium more efficiently. Some designs recycle tritium within the system. This reduces the need for external sources. Safety improvements also reduce the risk of leaks.
Sustainable Alternatives
Researchers explore ways to produce tritium without nuclear reactors. Methods include using particle accelerators to create tritium. These options lower radioactive waste and environmental impact. They also offer more control over production scale. Sustainable ways will help meet future demand safely.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Primary Method Of Producing Tritium?
Tritium is mainly produced in nuclear reactors by irradiating lithium-6 with neutrons. This reaction creates tritium and helium. It can also be generated in particle accelerators and during nuclear weapons testing.
How Long Does Tritium Production Take?
Tritium production depends on neutron flux and lithium target size. Typically, it takes several weeks in nuclear reactors to produce usable amounts. The process requires careful handling due to tritium’s radioactive nature.
Why Is Tritium Important In Industry And Research?
Tritium is vital for fusion energy, self-powered lighting, and scientific research. Its radioactive decay emits low-energy beta particles, useful in luminous devices and tracer studies. It also helps in nuclear weapon maintenance and environmental studies.
Can Tritium Be Produced Artificially Outside Reactors?
Yes, tritium can be made using particle accelerators by bombarding targets with high-energy particles. However, this method is less efficient and more expensive than reactor-based production. It is mainly used for small-scale or research purposes.
Conclusion
Tritium forms through nuclear reactions in special machines. Scientists carefully control these processes to create it safely. It plays an important role in energy and science fields. Understanding how tritium is made helps us see its value. This knowledge supports advances in clean energy and research.
Tritium’s unique properties make it useful in many ways. Simple steps combine to produce this rare element. Knowing the basics makes the topic easier to grasp. The process shows how science can shape our world.
Apply for this vacancy
For more information
For more information, please don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re here to assist with any questions or provide additional details to help you make informed decisions. Reach out today, and let’s connect!
Please mention the respective article number.
For more information
For more information, please don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re here to assist with any questions or provide additional details to help you make informed decisions. Reach out today, and let’s connect!
Please mention the respective article number.

