Have you ever wondered how some watches glow in the dark without needing a battery? Or how certain emergency exit signs stay visible even during power outages?
The secret behind these everyday miracles often involves something called tritium. Understanding tritium uses can open your eyes to fascinating technology that quietly powers safety, innovation, and even medical tools around you. Keep reading, and you’ll discover how this unique element might be playing a bigger role in your life than you realize.

Tritium Basics
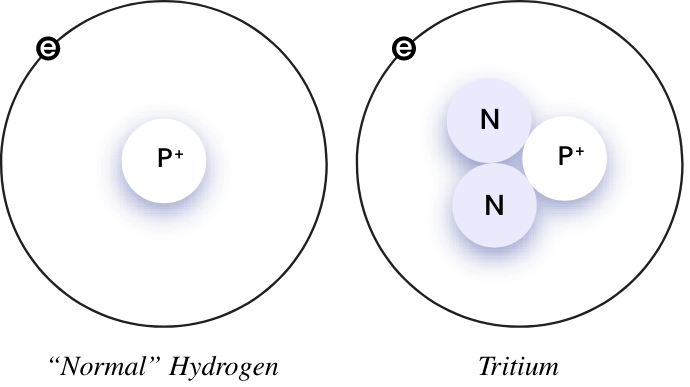
Tritium is a rare form of hydrogen. It has unique features that make it useful in many fields. Understanding tritium’s basics helps explain its importance. This section covers its main properties and where it comes from.
Properties And Characteristics
Tritium is a radioactive isotope of hydrogen. It has one proton and two neutrons in its nucleus. This makes it heavier than normal hydrogen. Tritium emits low-energy beta particles during decay. It has a half-life of about 12.3 years. It glows faintly in the dark when combined with phosphors. This glow is useful in self-luminous devices. Tritium is safe if handled properly because its radiation cannot penetrate skin.
Natural And Artificial Sources
Tritium forms naturally in the upper atmosphere. Cosmic rays hit nitrogen atoms, creating tritium. This natural tritium enters water and the environment. Most tritium used today is man-made. Nuclear reactors and particle accelerators produce it. It is collected for use in research and industry. Artificial tritium is purer and easier to control. Its production supports many scientific and commercial applications.
Energy Applications
Tritium plays an important role in energy production. Its unique properties make it useful for different energy technologies. Understanding these uses helps explain why tritium remains valuable.
Energy applications focus mainly on nuclear fusion and radioisotope power sources. These uses show tritium’s potential for clean and long-lasting energy.
Nuclear Fusion Potential
Tritium is key for nuclear fusion, a process that produces energy like the sun. Fusion combines light atoms, releasing large energy amounts. Tritium fuels fusion reactors by reacting with deuterium, another hydrogen form.
This reaction creates helium and neutrons, producing heat to generate electricity. Fusion using tritium could provide clean energy with little waste. Scientists work hard to develop safe and efficient fusion reactors using tritium fuel.
Radioactive Power Sources
Tritium powers radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs). These devices convert heat from radioactive decay into electricity. RTGs provide power in remote places where solar or batteries fail.
They are common in spacecraft, underwater vehicles, and emergency lighting. Tritium’s steady decay ensures a long-lasting energy supply. This makes it reliable for long missions or hard-to-reach locations.
Medical Uses
Tritium plays a key role in medicine. It helps doctors understand diseases better. Its unique properties make it useful in several medical fields. Tritium is safe to use in controlled amounts. It can track how drugs move inside the body. This helps improve treatments and save lives.
Radiolabeling In Diagnostics
Tritium is used to label molecules in the body. This process is called radiolabeling. It helps track how drugs or chemicals behave inside organs. Doctors use this to study diseases like cancer and infections. Tritium emits weak radiation that machines can detect. This helps create detailed images and data. It shows where a drug goes and how long it stays. This method improves accuracy in diagnosing illnesses.
Therapeutic Applications
Tritium also supports some treatments. It can be part of drugs that target damaged cells. These drugs deliver small doses of radiation to kill harmful cells. This helps reduce side effects compared to other treatments. Tritium’s radiation is gentle but effective at close range. It is useful in treating certain cancers and infections. Scientists continue to explore new ways to use tritium in therapy.

Illumination Technologies
Tritium plays a key role in many illumination technologies. It is a safe, glowing gas used in many devices. Tritium’s light does not need batteries or electricity. This makes it useful in places where power is not available or practical.
Its glow is steady and easy to see in the dark. Many industries use tritium to help people see clearly and stay safe at night.
Self-luminous Devices
Tritium is used in self-luminous devices that glow without light sources. Watches with tritium hands shine in the dark. They help people tell time easily at night or underwater.
Other devices include exit signs and safety markers. These glow continuously for years without needing power. This helps guide people during power outages or emergencies.
Safety And Longevity
Tritium is safe when sealed inside glass tubes. It emits low-energy radiation that cannot harm the skin. This makes it safe for everyday use in homes and public places.
Tritium lights last for many years. Their glow slowly fades but can shine for over a decade. This long life reduces the need for replacements and maintenance.
Environmental Impact
Tritium is a radioactive form of hydrogen used in many industries. Its environmental impact is a key concern. Tritium can enter water and air, affecting living things. Understanding how to handle and dispose of it safely is important. Strict rules help protect the environment from harm caused by tritium.
Handling And Disposal
Tritium must be handled with care. It can leak into water or soil if not managed properly. Safe storage containers prevent leaks and spills. Disposal requires special methods to avoid pollution. Facilities use sealed tanks to hold tritium waste. They monitor these sites regularly for any signs of leakage. Proper handling reduces the risk of environmental damage.
Regulations And Safety Measures
Governments set strict rules for tritium use. These laws control how much tritium can be released. Safety measures include regular inspections and worker training. Companies must report any spills or accidents immediately. Limits on emissions protect water and air quality. These regulations help keep communities and nature safe from harm.
Future Innovations
Tritium holds promise for many future innovations. Its unique properties make it valuable for science and technology. Researchers explore new ways to use tritium in energy and industry. These efforts aim to create safer and cleaner technologies. The future of tritium looks bright with ongoing studies and experiments.
Advances In Fusion Research
Tritium plays a key role in fusion energy research. Fusion aims to produce power by combining atomic nuclei. Tritium acts as a fuel in fusion reactors. Scientists work to improve fusion reactor designs using tritium. Better control of tritium can increase energy output. These advances may lead to efficient and clean energy sources.
Emerging Tech Opportunities
Tritium offers new chances in various technologies. It is used in self-powered lighting and safety signs. Emerging tech explores tritium in medical and environmental fields. Researchers test tritium for detecting leaks and pollution. Future devices may use tritium for long-lasting power. These opportunities expand tritium’s role beyond current uses.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Primary Uses Of Tritium Today?
Tritium is mainly used in self-luminous devices like watch dials and exit signs. It also serves in nuclear fusion research and as a tracer in environmental studies. Its radioactive glow makes it ideal for low-light applications without external power sources.
How Does Tritium Enhance Safety In Emergency Signs?
Tritium provides continuous illumination in emergency signs without electricity. Its radioactive decay emits light, ensuring visibility during power outages. This makes tritium-based signs reliable for guiding people to exits safely in dark or smoky conditions.
Why Is Tritium Important In Nuclear Fusion Research?
Tritium acts as a fuel in nuclear fusion reactors. It combines with deuterium to release enormous energy. This reaction is crucial for developing clean, sustainable energy sources, making tritium vital in fusion experiments and future energy solutions.
Can Tritium Be Used In Medical Or Environmental Applications?
Yes, tritium is used as a radioactive tracer in medical and environmental research. It helps track biological processes and pollutant movements. Its ability to label molecules without altering them makes tritium valuable for scientific studies.
Conclusion
Tritium has many practical uses in daily life and industry. It helps power watches, signs, and scientific tools. Its role in nuclear energy and medicine is important too. Safe handling is key to using tritium well. Understanding its benefits and risks can guide smart use.
Tritium remains a valuable resource in modern technology and research. It shows how science helps improve many things around us.
Apply for this vacancy
For more information
For more information, please don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re here to assist with any questions or provide additional details to help you make informed decisions. Reach out today, and let’s connect!
Please mention the respective article number.
For more information
For more information, please don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re here to assist with any questions or provide additional details to help you make informed decisions. Reach out today, and let’s connect!
Please mention the respective article number.

